Conversational commerce is shifting from experiment to expectation. Buyers increasingly want to discover products, refine choices, and complete purchases inside an AI-driven conversation, without navigating a traditional storefront. The question for enterprise brands isn’t if this channel matters, but how to enable it without compromising the integrity, security, and scalability of the commerce core.
The XCentium ACP Cartridge provides a clean, extensible pattern to connect ChatGPT (or any ACP-aware client) with Salesforce AgentForce Commerce formerly known as Salesforce Commerce Cloud (SFCC) through ACP-style HTTPS endpoints exposed via a custom SFRA controller layer, supported by a lightweight Node.js proxy. Your SAFC instance remains the system of record for catalog, pricing, promotions, taxation, and order lifecycle, while ChatGPT becomes the conversational experience layer.
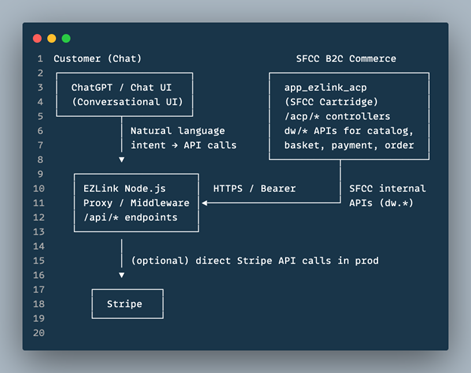
This article explains the architecture and implementation approach from a principal-architecture lens, grounded in the POC details and aligned with standard SAFC platform capabilities.
What the XCentium ACP Cartridge Is?
The XCentium ACP Cartridge (app_xcentium_acp) is an SAFC cartridge that introduces ACP-style controllers under /acp/*, specifically designed to serve conversational clients. It works in tandem with a Node.js service that provides friendly /api/* endpoints, which ChatGPT or a chat UI can use as the external contract.
This two-layer approach intentionally separates:
- Conversation-facing API ergonomics (Node.js)
- Commerce-authoritative business logic (SAFC cartridge)
It also enables mocked development and faster iteration cycles before integrating with a real SAFC environment.
Why This Pattern Matters
1) It Protects the Commerce Core
SAFC remains the authoritative engine for:
- Product search behavior (via ProductSearchModel)
- Basket creation and orchestration (BasketMgr)
- Shipping choices (ShippingMgr)
- Payment instrumentation (PaymentMgr)
- Order lifecycle (OrderMgr)
- Promotions and tax calculation via standard basket calculation flows
The conversational layer does not rewrite your storefront and does not replace your core processes. Instead, it surfaces them through a stable API contract that aligns with how agentic clients naturally operate.
2) It Reduces Channel Coupling
The ACP endpoints become a channel-neutral contract. You can reuse the same endpoints across:
- ChatGPT
- A branded chat UI
- Mobile apps
- Kiosks
- Future agentic platforms
3) It Avoids “One-Big-Integration” Risk
The Node.js layer gives you flexibility to add:
- Observability
- Rate limiting
- Caching
- Error normalization
- Feature flags
- Stripe orchestration
All without repeated SAFC deployments.
High-Level Architecture
XCentium introduces three major components:
- ChatGPT / ACP Client
- Understands intent.
- Calls HTTP tools.
- Maintains conversational context like sessionId and orderNo.
- XCentium Node.js Service
- Exposes /api/products, /api/checkout, /api/payment, /api/orders, /api/health.
- Supports two modes:
- Mock mode (USE_MOCK=true) with local JSON and in-memory state.
- Live mode (USE_MOCK=false) that proxies to SFCC.
- XCentium ACP SFCC Cartridge
- Implements:
- EZACPProducts
- EZACPCheckout
- EZACPPayment
- Uses standard SFCC dw.* APIs.
- Implements:
This design keeps the system intentionally simple while offering clear paths for production hardening.
End-to-End Flow: Customer → ChatGPT → Node → SFCC → (Stripe) → Order
1) Product Discovery
ChatGPT calls:
- GET /api/products?q=shirt&limit=10
Node behavior:
- Mock Mode: reads ./mock/products.json, filters, returns results.
- Live Mode: calls:
- GET {SFCC_BASE}/acp/products?q=shirt&limit=10
SFCC behavior:
- Uses ProductSearchModel and returns a normalized, conversation-friendly schema:
- id, name, description, price, currency, image, url, available, brand, categoryId.
This is intentionally minimal to reduce noise and improve conversational clarity.
2) Checkout Session Creation
ChatGPT calls:
- POST /api/checkout { items, shippingAddress, shippingMethodID }
Node (live) proxies to:
- POST /acp/checkout
SFCC (checkout session script/controller) performs:
- Basket creation or reset.
- Item validation (existence, online status, orderability).
- Quantity placement.
- Shipping address population.
- Shipping method application and fallback logic.
- BasketMgr.calculateBasket() to trigger:
- promotions
- tax calculation
- shipping cost evaluation
Return payload includes:
- sessionId
- basketId
- quote:
- totals and line items
This is the pivotal step that makes the conversational flow deterministic and auditable.
3) Payment and Order Creation
ChatGPT calls:
- POST /api/payment
Node (live) proxies to:
- POST /acp/payment
In the POC, SFCC uses paymentFake.js for simulation:
- Fake card rules
- Creates a payment instrument
- Creates and places a real SFCC order
- Returns:
- status: 'paid'
- orderNo
- psp object referencing the fake provider
This demonstrates the lifecycle without claiming a production PCI stance.
The POC Boundary
What POC confirms:
- The ACP-style contract can cleanly drive core commerce flows.
- SFCC can remain the system of record even when the “front end” is ChatGPT.
- The Node layer can accelerate development via mock-first workflows.
- Real orders can be created in Business Manager through this conversational path.
What is explicitly not production-ready by design:
- Raw card data handling (POC only).
- Idempotent payment protections.
- Full observability and structured logging.
- Advanced edge cases (multi-shipping, complex B2B pricing, multi-currency expansions beyond standard site defaults).
Installation and Configuration Essentials
Cartridge Placement
Structure is clear and aligned with SFRA conventions:
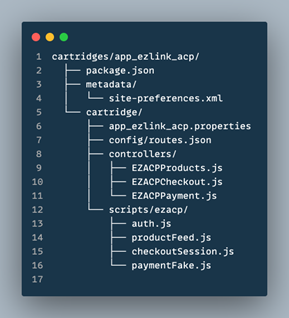
Cartridge Path
Ensure app_xcentium_acp is first:
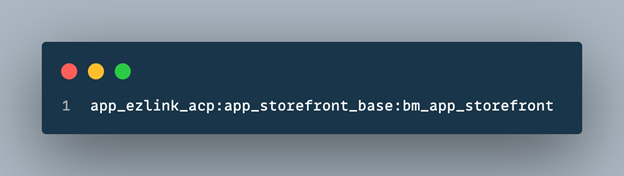
This ensures ACP controllers resolve ahead of base storefront routing.
Site Preferences
Core preferences for environment control and security:
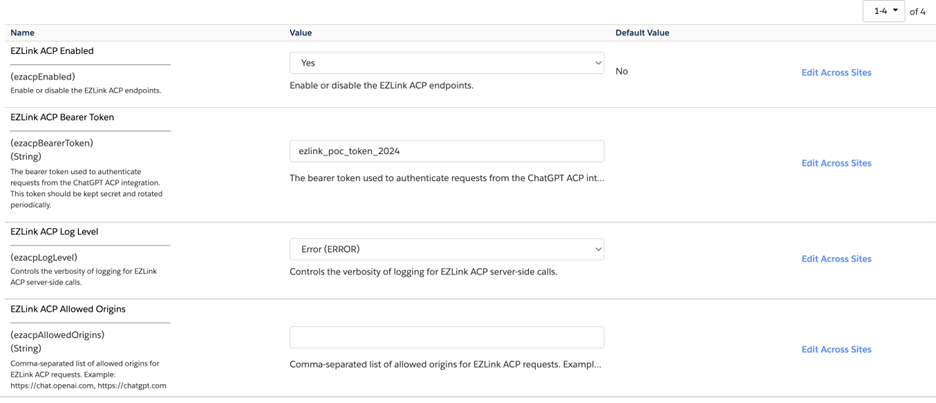
- ezacpEnabled
- ezacpBearerToken
- ezacpLogLevel
- ezacpAllowedOrigins
Note: The POC default token must be replaced in any real environment.
Node.js Service Setup
Your Node service aligns with a pragmatic integration strategy:
- Minimal dependencies:
- express
- node-fetch (ESM)
Environment Modes
Mock mode (default):
- Ideal for:
- UI development
- conversational design
- early demos
- integration test harness creation
Live mode:
- Enforces:
- SFCC_BASE
- ACP_TOKEN
Why This Layer Is Strategic
As a program-level design choice, this Node tier is more than a proxy:
- It’s your edge control plane for conversational traffic.
- It decouples release velocity.
- It can evolve into:
- caching
- A/B testing
- fine-grained rate limits
- correlation-based logging
- centralized error governance
Stripe: Two Production-Grade Models
The architectural decision here will be driven by PCI scope appetite and ownership of the payment experience.
Model 1: ChatGPT-Hosted Stripe Checkout (PCI-Minimizing)
This is the cleanest risk boundary:
- The customer enters card details directly into Stripe-controlled UI.
- Node and SFCC never receive raw card data.
- The conversation returns:
- paymentIntentId (or token equivalent)
- SFCC finalizes the order after verifying:
- status
- amount
- currency
This model aligns with a minimal PCI footprint and a more modern agentic payment experience.
Model 2 — SFCC Server-Side Stripe Integration
This is consistent with SFCC’s standard external PSP integration patterns:
- Use LocalService Registry.
- Implement a service wrapper script (e.g., for Payment Intent creation/confirmation).
- Store only token/intent references inside SFCC payment instruments.
The key program risk here is not feasibility—it’s governance:
- idempotency
- error mapping
- timeout behavior
- 3DS flows (if needed)
- operational monitoring
Idempotency and Order Safety
The POC’s stated constraint is correct:
- /acp/payment is not idempotent in its current state.
For production hardening:
- Use a unique Stripe Payment Intent or delegated token.
- Persist it on the order/payment instrument.
- Reject duplicates for the same token.
- Optionally introduce a separate:
- /acp/payment/complete
This separation supports out-of-band payment completion flows and is highly aligned with conversational UX timing.
Security and Compliance Layering
The most crucial architectural rule remains non-negotiable:
Never send raw card data to SFCC in production.
Instead:
- Tokenize client-side via Stripe-hosted UI or approved client-side patterns.
- Pass only delegated references through ACP.
Other hardening priorities:
- Bearer token rotation strategy
- CORS governance via trusted origins
- Rate limiting at Node and/or edge
- Logging redaction:
- no Authorization headers
- no full PII dumps
- no payment credentials
QA Strategy That Matches Enterprise Expectations
Production readiness discipline:
- Product search testing
- Checkout session correctness
- POC payment simulation correctness
- Negative-path and auth testing
- Performance and burst behavior
For scaling confidence:
- Add test harnesses that simulate:
- multi-turn conversational state reuse
- partial checkout updates
- concurrent session creation under load
Business Value and KPI Framing
From an executive view, this pattern addresses three high-value levers:
- Higher conversion through guided discovery
- AOV uplift via conversational upsell
- Reduced friction between intent and purchase
This isn’t a “chat widget.” It’s an architectural channel extension that preserves existing SFCC investments while enabling new AI-first experiences.
Practical Roadmap: From POC to Production
SFCC Hardening
- Formalize ACP schema contracts.
- Add order custom attributes for channel traceability:
- acpSessionId
- acpChannel
- acpPaymentIntentId
- Introduce a real Stripe service integration pattern if choosing Model 2.
- Integrate with existing hooks (e.g., afterOrderPlaced) for downstream systems.
Node Hardening
- Implement:
- structured logging
- correlation IDs
- rate limiting
- standardized error envelopes
- Add deployment automation and environment gating.
Conversational Layer Hardening
- Build robust tool definitions that:
- preserve session context safely
- prompt for missing attributes
- avoid price/availability commitments until confirmed by ACP
Final Takeaway
The XCentium ACP Cartridge is an excellent example of how to enable ChatGPT-as-a-storefront without destabilizing enterprise commerce foundations.
- Respects SFCC as the system of record.
- Separates conversational experience from commerce execution.
- Uses familiar SFRA controller mechanics and standard dw.* services.
- Enables mock-first development for speed and clarity.
- Creates a clean runway for Stripe integration under real compliance rules.

